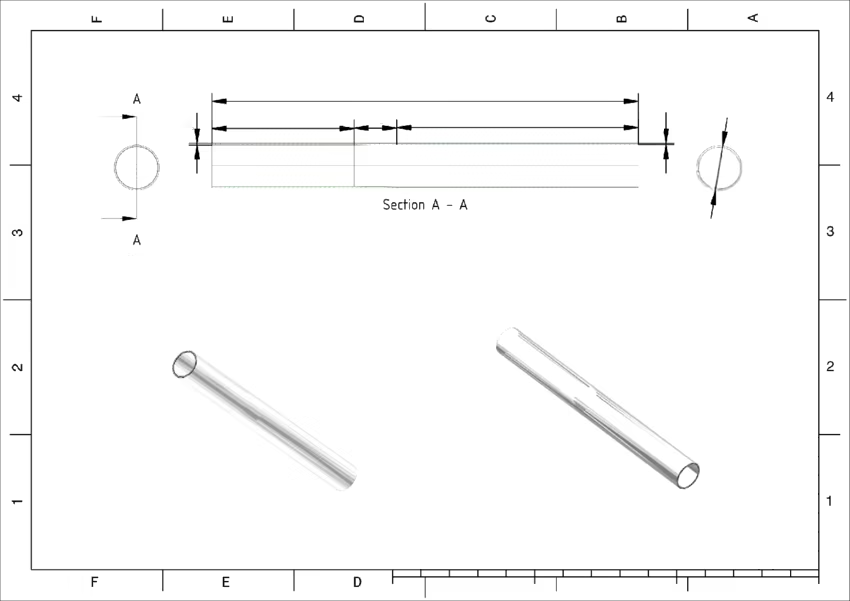
Steel Tube Machining
Steel tube machining is a critical process in various industries, including construction, automotive, and manufacturing. It involves shaping and modifying steel tubes to meet specific requirements and tolerances. This article will explore the fundamentals of steel tube machining, the methods involved, and the materials suitable for machining.
What is Steel Tube Machining?
Steel tube machining refers to the process of cutting, shaping, and finishing steel tubes to achieve desired dimensions and specifications. This process is essential for creating components that fit precisely into larger assemblies or systems. Machining ensures that steel tubes meet the necessary standards for strength, durability, and functionality.
What are the Methods of Steel Tube Machining?
Several methods are employed in steel tube machining, each serving a specific purpose:
-
Sawing: This is the process of cutting steel tubes to length using saws. It is a fundamental step in machining, allowing for precise cuts and efficient material usage.
-
Chamfering: Chamfering involves beveling the edges of steel tubes. This method is crucial for removing sharp edges, improving safety, and preparing the tubes for welding or assembly.
-
Bending: Bending is used to shape steel tubes into specific angles or curves. This method is essential in applications where tubes need to fit into complex geometries.
-
CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining involves using computer-controlled machines to perform precise cuts, drills, and other modifications. CNC machining is highly accurate and allows for complex designs and tight tolerances.
What Material of Steel Tube is Suitable for Machining?
The suitability of a steel tube for machining depends on its composition and properties. Common materials include:
-
Carbon Steel: Known for its strength and affordability, carbon steel is widely used in machining. It is suitable for applications requiring durability and resistance to wear.
-
Stainless Steel: This material is chosen for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Stainless steel is ideal for applications in harsh environments or where hygiene is a concern.
-
Alloy Steel: Alloy steels contain additional elements like chromium, nickel, or molybdenum, enhancing their mechanical properties. They are suitable for high-stress applications.
-
Tool Steel: Known for its hardness and resistance to abrasion, tool steel is used in applications requiring cutting or shaping tools.
Conclusion
Steel tube machining is a vital process that involves various methods to achieve precise and functional components. Sawing, chamfering, bending, and CNC machining are key techniques used to modify steel tubes. The choice of material, whether carbon, stainless, alloy, or tool steel, depends on the specific requirements of the application. Understanding these aspects ensures that steel tubes are machined effectively, meeting the demands of diverse industries.