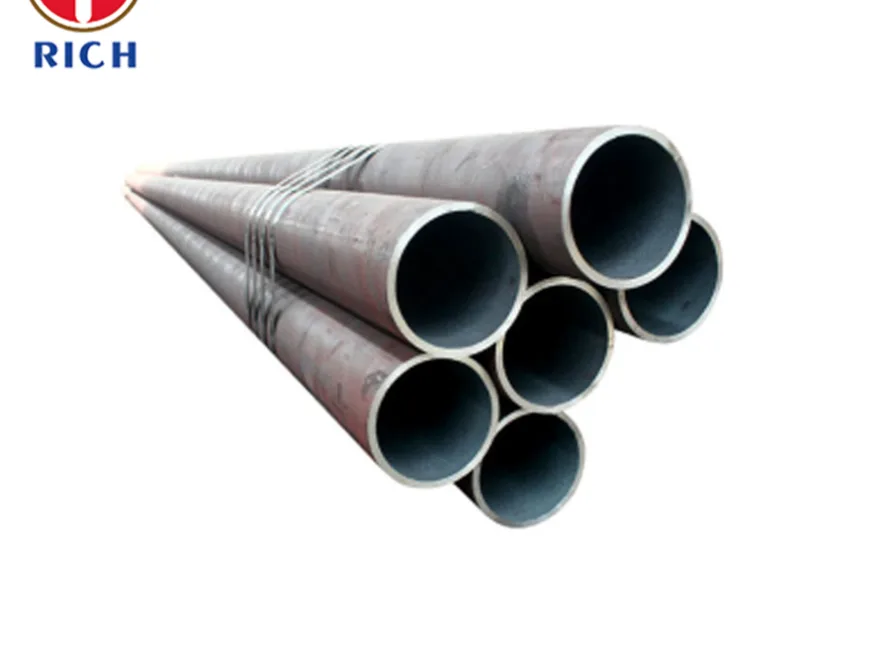
Description
EN 10305-2 E195 Cold Drawn Welded Precision Steel Tubes
Material
EN 10305-2 specifies cold drawn welded (CDW) precision steel tubes, widely used in automotive, mechanical engineering, and precision applications. The tubes are produced by welding hot rolled strip steel, followed by cold drawing to achieve tight dimensional tolerances, smooth surfaces, and enhanced mechanical properties.
Specifications
-
Standard: EN 10305-2
-
Grades: E195 (1.0034), E235 (1.0308), E275 (1.0225), E355 (1.0580), S500MC (1.0984)
-
Process: Cold Drawn, Welded
-
Shape: Round, Square, Rectangular
-
Surface: Bright, Clean, Oiled or Phosphated
-
Delivery condition: +C (cold drawn/hard), +LC (annealed), +SR (stress-relieved), +A (annealed), +N (normalized)
Chemical Composition
| Grade | C max | Si max | Mn max | P max | S max | Al min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E195 (1.0034) | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.55 | 0.025 | 0.025 | – |
| E235 (1.0308) | 0.17 | 0.35 | 1.20 | 0.025 | 0.025 | – |
| E275 (1.0225) | 0.21 | 0.35 | 1.40 | 0.025 | 0.025 | – |
| E355 (1.0580) | 0.22 | 0.55 | 1.60 | 0.025 | 0.025 | – |
| S500MC (1.0984) | 0.12 | 0.60 | 1.70 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 0.015 |
Mechanical Properties
| Grade | Yield Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation A5 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| E195 (1.0034) | ≥195 | 320–440 | ≥28 |
| E235 (1.0308) | ≥235 | 340–480 | ≥25 |
| E275 (1.0225) | ≥275 | 410–560 | ≥21 |
| E355 (1.0580) | ≥355 | 490–630 | ≥22 |
| S500MC (1.0984) | ≥500 | 550–700 | ≥16 |
Key Features
-
High dimensional accuracy and tight tolerances
-
Smooth surface suitable for machining and finishing
-
Good weldability and formability
-
Excellent mechanical performance depending on grade
-
Available in various heat treatment conditions
Standards
-
EN 10305-2: Cold drawn welded precision steel tubes
-
Equivalent references:
-
ASTM A513 (Type 5 DOM Tubes)
-
JIS G3472 / JIS G3445 (Automotive tubes)
-
GB/T 3639 (Cold drawn precision tubes)
-
GOST 10704 / 10705 (Welded tubes, precision application variants)
-
Applications
Cold drawn welded tubes are widely used in:
-
Automotive industry: steering columns, shock absorber components, chassis parts, seat structures
-
Mechanical engineering: hydraulic cylinders, precision shafts, bearings sleeves, drive shafts
-
Furniture: office chair frames, steel furniture tubes
-
General engineering: conveyor rollers, telescopic systems, machine frames
In automotive: applied in safety-critical components such as steering systems and seat reinforcements.
In hydraulics: used as cylinder tubes requiring precision ID/OD.
In furniture: used for aesthetic, lightweight yet strong tubular structures.