Description
Alloy Steel Pipe Fittings ASTM A182
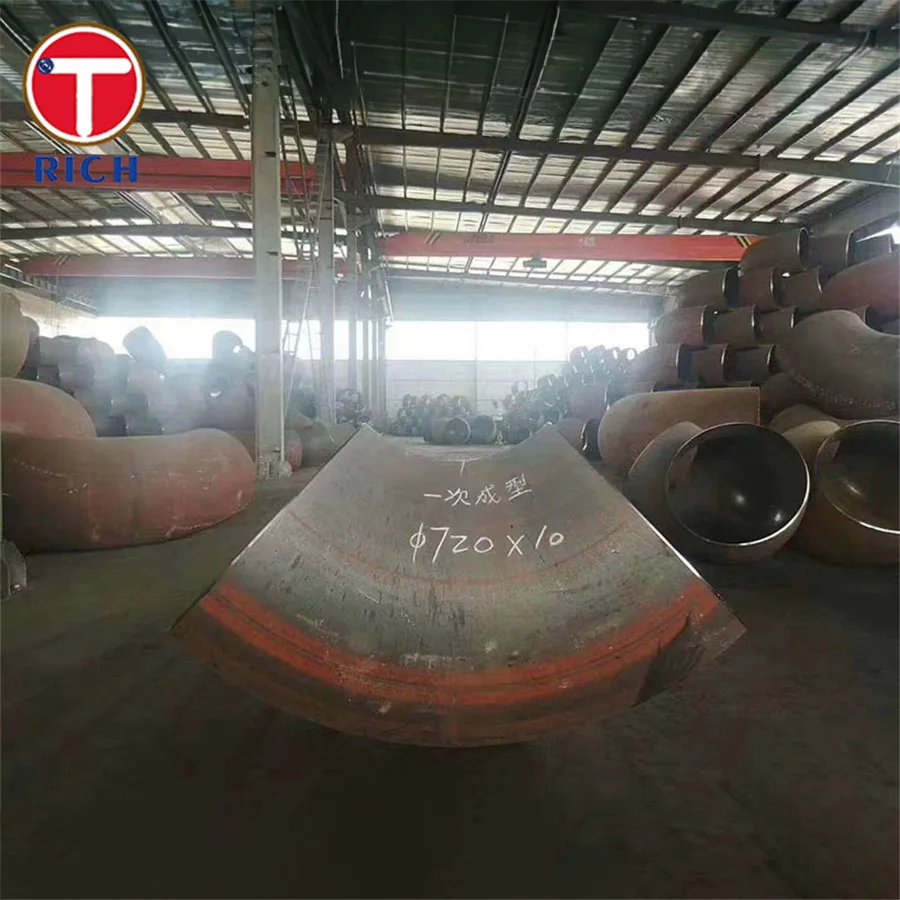
Alloy steel pipe fittings are an essential component in various industries, providing a reliable and durable connection between pipes. One widely used standard for alloy steel pipe fittings is ASTM A182. In this article, we will explore the material, drawing format, production process, surface roughness, treatment, inspection instrument, and application of alloy steel pipe fittings manufactured according to ASTM A182.
Material
ASTM A182 specifies several grades of alloy steel suitable for pipe fittings, including but not limited to:
- F1 – Martensitic alloy steel
- F5 – Chromium-molybdenum alloy steel
- F9 – Chromium-molybdenum alloy steel
- F11 – Chromium-molybdenum alloy steel
- F22 – Chromium-molybdenum alloy steel
- F91 – Chromium-molybdenum alloy steel
These grades offer excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature performance, making them suitable for various demanding applications.
Drawing Format
The drawing format for alloy steel pipe fittings follows industry standards, including detailed dimensions, tolerances, and specifications. These drawings provide manufacturers with the necessary information to produce fittings that meet the required specifications and ensure proper fitment.
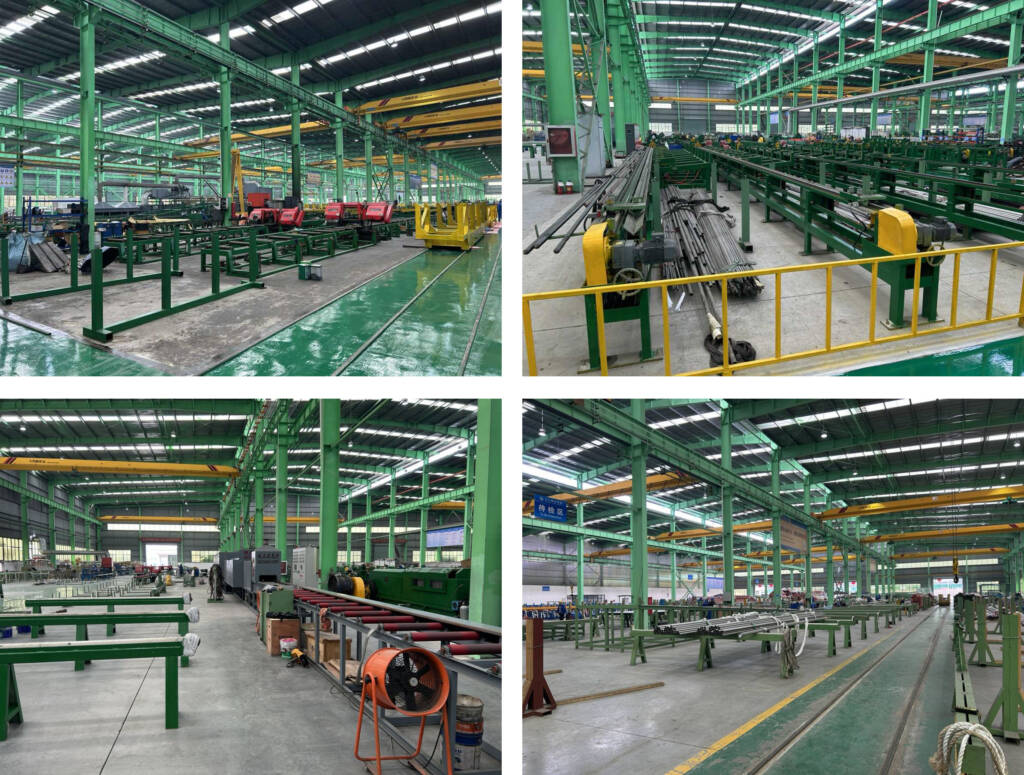
Production Process
The production process of alloy steel pipe fittings involves several steps:
- Material selection: The appropriate grade of alloy steel is chosen based on the application requirements.
- Heating and forming: The selected alloy steel is heated to a suitable temperature and then formed into the desired shape using forging or machining techniques.
- Machining and finishing: The fittings are further machined to achieve the required dimensions and surface finish.
- Heat treatment: To enhance the mechanical properties of the fittings, they undergo heat treatment processes such as annealing, normalizing, or quenching and tempering.
- Surface treatment: The fittings may undergo surface treatments like shot blasting, pickling, or passivation to improve their corrosion resistance and appearance.
- Inspection and testing: The fittings are thoroughly inspected to ensure they meet the required specifications and quality standards.
- Packaging and delivery: The finished fittings are carefully packaged and delivered to the customers.
Surface Roughness and Treatment
The surface roughness of alloy steel pipe fittings is an important factor that affects their performance and appearance. The specific surface roughness requirements may vary depending on the application and customer specifications. Common surface treatments include shot blasting, grinding, polishing, or coating to achieve the desired surface finish and improve corrosion resistance.
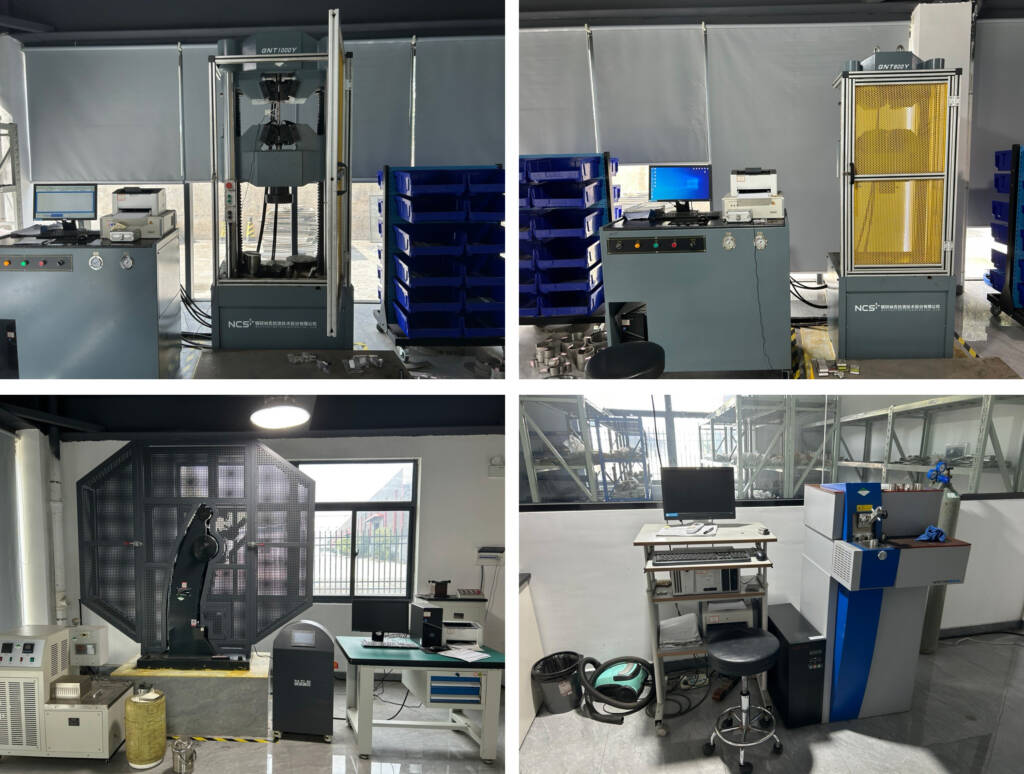
Inspection Instrument
To ensure the quality and dimensional accuracy of alloy steel pipe fittings, various inspection instruments are used during the manufacturing process. These instruments include:
- Calipers and micrometers: Used to measure dimensions and tolerances.
- Coordinate measuring machines (CMM): Used for precise dimensional measurements.
- Ultrasonic testing equipment: Used to detect internal defects or inconsistencies.
- Hardness testers: Used to determine the hardness of the fittings.
- Visual inspection tools: Used to visually inspect the surface finish and overall quality.
Application
Alloy steel pipe fittings manufactured according to ASTM A182 find applications in a wide range of industries, including:
- Oil and gas: Used in pipelines, refineries, and petrochemical plants.
- Power generation: Used in power plants for steam and gas applications.
- Chemical processing: Used in chemical plants for handling corrosive fluids.
- Shipbuilding: Used in marine applications for their high strength and corrosion resistance.
- Construction: Used in structural applications that require high strength and durability.
In conclusion, alloy steel pipe fittings manufactured according to ASTM A182 offer excellent mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature performance. The material, drawing format, production process, surface roughness, treatment, inspection instruments, and applications discussed in this article provide a comprehensive overview of these fittings.