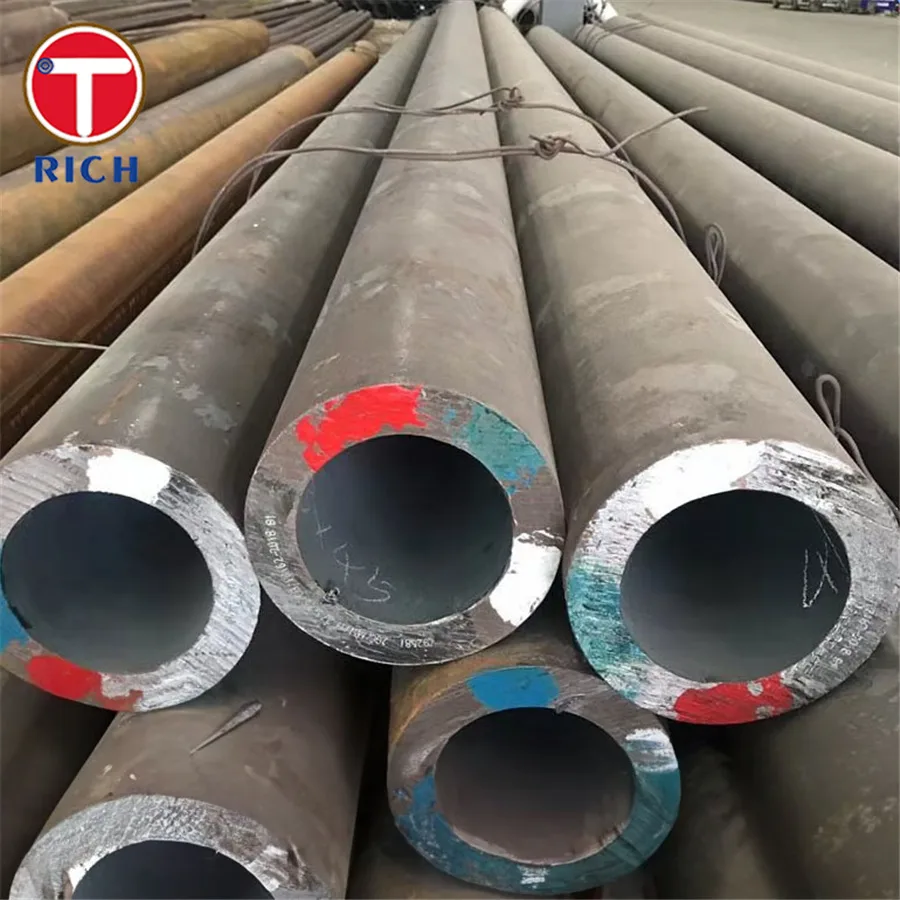
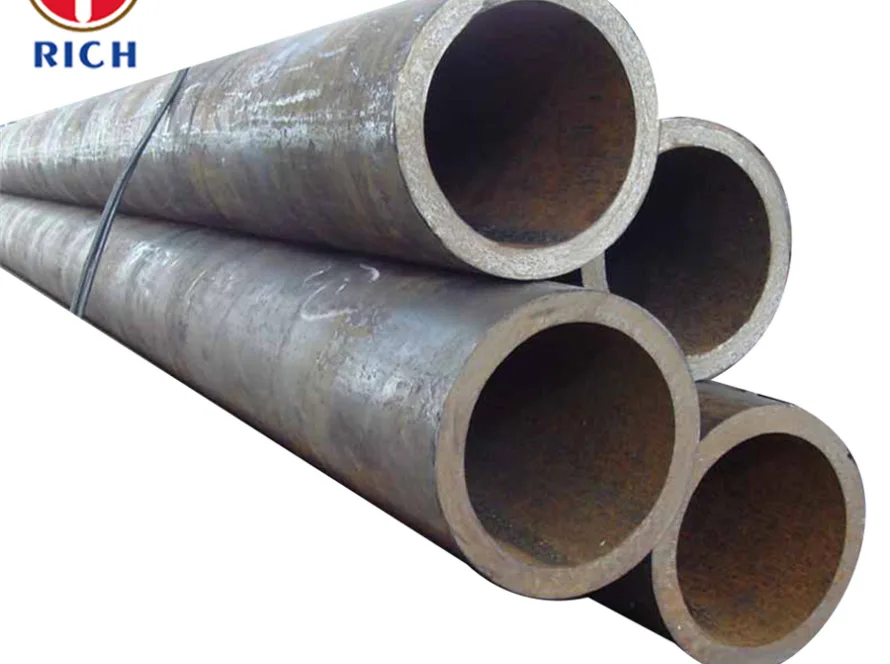
Description
DIN 1629 St37 (1.0254) St44 (1.0256) St52 (1.0421) Carbon Seamless Steel Tube
Introduction
DIN 1629 is a standard specification for carbon seamless steel tubes used in various industrial applications. This article provides an overview of DIN 1629 St37, St44, and St52 steel tubes, including their material composition, key features, mechanical properties, and applications. Additionally, alternative grades that can be considered as substitutes will be discussed.
Material and Specification
DIN 1629 St37, St44, and St52 steel tubes are made from carbon steel and are produced using the seamless process. These tubes are designed for high-temperature and high-pressure applications, ensuring reliable performance in demanding environments. The material specifications for each grade are as follows:
- St37 (1.0254): This grade has a minimum tensile strength of 340 N/mm² and a minimum yield strength of 235 N/mm². It is characterized by excellent weldability and good machinability.
- St44 (1.0256): With a minimum tensile strength of 410 N/mm² and a minimum yield strength of 275 N/mm², St44 offers improved mechanical properties compared to St37. It is suitable for applications requiring higher strength.
- St52 (1.0421): St52 has a minimum tensile strength of 490 N/mm² and a minimum yield strength of 355 N/mm². It exhibits excellent impact resistance and is often used in structural applications.
Key Features
- Carbon seamless steel tubes: DIN 1629 St37, St44, and St52 tubes are manufactured using the seamless process, ensuring a uniform and consistent structure throughout the tube.
- High-temperature resistance: These tubes are designed to withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for applications involving heat transfer or exposure to elevated temperatures.
- High-pressure capabilities: DIN 1629 steel tubes are capable of withstanding high-pressure environments, making them ideal for applications in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemicals, and power generation.
- Versatile and reliable: The seamless construction of these tubes ensures a high level of reliability and eliminates the risk of leakage or failure at welded joints.
Chemical Composition
| Grade | C% (max) | Si% (max) | Mn% | P% (max) | S% (max) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| St37 | 0.17 | 0.35 | 0.35-0.65 | 0.040 | 0.040 |
| St44 | 0.21 | 0.35 | 0.40-1.20 | 0.040 | 0.040 |
| St52 | 0.22 | 0.55 | 1.60-2.00 | 0.040 | 0.040 |
Mechanical Properties
| Grade | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) | Elongation (%) | Impact Energy (J) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| St37 | 340-470 | 235 | 25 | – |
| St44 | 410-540 | 275 | 21 | – |
| St52 | 490-630 | 355 | 22 | 27 |
Steel Grade and Application
- St37: This grade is commonly used in general structural applications, such as buildings, bridges, and machinery components.
- St44: St44 finds its application in the construction of pressure vessels, boilers, and pipelines, where higher strength is required.
- St52: St52 is widely used in the manufacturing of mechanical components, such as hydraulic cylinders, automotive parts, and machinery components.
Possible Alternative Grades
While DIN 1629 St37, St44, and St52 are widely used, there are alternative grades available that can be considered based on specific requirements. Some possible alternative grades include ASTM A106 Grade B, ASTM A53 Grade B, and API 5L Grade B. These grades have similar chemical compositions and mechanical properties, making them suitable substitutes in certain applications.